Suite à la prolifération de clones qui sont à garder plusieurs mois en cas de besoin de retour en arrière nous cherchions une solution de deduplication.
Apres avoir testé :
- Le ZFS avec deduplication de Freenas
(Taux non satisfaisant) - OpenDedup : Projet opensource de deduplication
(Codé sous JAVA, trop complexe à maintenir)
Nous nous sommes tourné vers Windows 2012 R2 offrant ce service.
A savoir que ce n’est pas une dedup à la volée, c’est à dire que l’espace de stockage doit être initialement disponible à la copie des fichiers afin que le service passe sur les blocs pour dedupliquer les doublons en tâche planifiée.
Recommandations Microsoft
Server and volume requirements for deduplication
Servers
See the following list for server requirements for deduplication:
- Server hardware should meet the minimum requirements for running Windows Server 2012. The deduplication feature was designed to support minimal configurations such as a single processor system with 4 GB of RAM and one SATA hard disk drive.
- If you plan to support deduplication on multiple volumes on the same server, you need to plan an appropriately size for the system to ensure that it can process the data. The general rule is that the server needs 1 CPU-core and 350 MB of free memory to run a deduplication job on a single volume, and that job can process about 100 GB per hour or around 2 TB per day. Deduplication scales with additional CPU core processors and available memory to enable parallel processing of multiple volumes.For example: If you have a server with 16 CPU core processors and 16 GB of memory, deduplication uses 25% of the system memory in the default Background Processing mode, and in this case, that would be 4 GB. If you divide by 350 MB, you can calculate that the server could process about 11 volumes at a time. If you add 8 GB of memory, the system could process 17 volumes at a time. If you set an optimization job to run in Throughput mode, the system will use up to 50% of the system’s memory for the optimization job.
- Data Deduplication supports up to 90 volumes at a time; however, deduplication can simultaneously process one volume per physical CPU core processor plus one. Hyper-threading does not impact this because only physical core processors can be used to process a volume. A system with 16 CPU core processors and 90 volumes will process 17 volumes at a time until all 90 volumes are done, if there is sufficient memory.
- Virtual server instances should follow the same guidance as physical hardware regarding server resources.
Volumes
Volumes that are candidates for deduplication must conform to the following requirements:
- Must not be a system or boot volume. Deduplication is not supported on operating system volumes.
- Can be partitioned as a master boot record (MBR) or a GUID Partition Table (GPT), and must be formatted using the NTFS file system.
- Can reside on shared storage, such as storage that uses a Fibre Channel or an SAS array, or when an iSCSI SAN and Windows Failover Clustering is fully supported.
- Do not rely on Cluster Shared Volumes (CSVs). You can access data if a deduplication-enabled volume is converted to a CSV, but you cannot continue to process files for deduplication.
- Do not rely on the Microsoft Resilient File System (ReFS).
- Can’t be larger than 64 TB in size.
- Must be exposed to the operating system as non-removable drives. Remotely-mapped drives are not supported.
Installer votre serveur Windows 2012 et faites un Windows Update avant toute chose.
Installer le rôle
- Ajouter rôle et fonctionnalité (EN: Add Roles and Features)
- Naviguer jusque “rôle de serveurs”
- Sous “Services de fichiers et de Stockage” (File and Storage Services role)
– Ouvrir “Services de fichiers et iSCSI” ( File and iSCSI Services)
– sélectionner “Deduplications des données” (Data Deduplication) 
- Suivant
- Suivant (Ne pas ajouter de fonctionnalités)
- Installer
Configuration du volume
- Dans le “Gestionnaire de serveur”
- Services de fichiers et de stockage
- Sous Volumes sélectionner la partition dédié à la deduplication et cliquer sur “Configurer la Déduplication des données…”

Pour contrôler l’état du JOB
get-dedupjob
Pour contrôler le taux de deduplication
get-dedupstatus
Ou via la console de gestion du serveur
Dans “Services de fichiers et de Stockage”
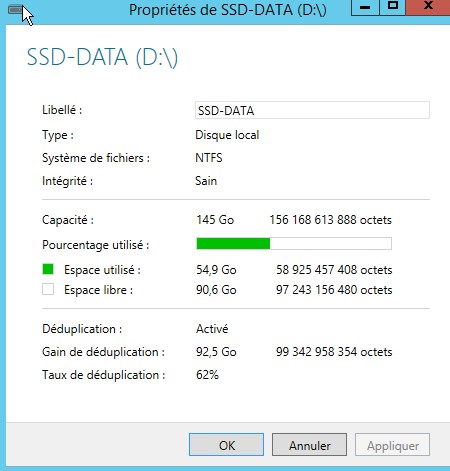
SSD avec VMs de LAB
Taux a 62%
Partition de sources (ISO, OVF, …)
Taux à 44 %
Clic droit / Propriété sur la partition SSD contenant nos VMs
Nous voyons espace utilisé 55 Go mais si on fait un clic droit / propriéte sur le dossier avec les VMs nous avons 144 Go Utilisés
Hehehehe pas mal
Next Step :
Creation du serveur NFS sous Windows 2012 R2
http://vroomblog.com/tuto-serveur-nfs-sous-windows-2012-r2/
Comment monter un partage NFS sur ESXi
http://vroomblog.com/ajouter-un-partage-nfs-sur-un-esxi/










[…] http://vroomblog.com/tuto-deduplication-sous-windows-2012-r2/ […]
Bonjour,
Avez-vous la procédure pour supprimer définitivement la dedup sur un Windows 2012 R2 et supprimer les fichiers inutiles avec un Garbage Collector ?
Quelles précautions sont à prendre sur un serveur en production ?
Merci beaucoup. Les diverses explications sur le net ne sont pas très satisfaisantes au contraire de vos explications précises.